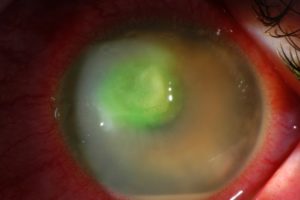
SYMPTOMS
Redness, foreign body sensation, pain, light sensitivity, discharge, mild to severe decreased vision.
CAUSES
Typical causes are bacteria, fungi or a parasite such as acanthamoeba.
RISK FACTORS
Contact lens wear, eye trauma and certain corneal conditions including ocular surface disease and prior corneal surgery.
COMPLICATIONS
Corneal ulceration; glaucoma; corneal thinning, scarring and irregularity; corneal neovascularization; cataract formation; corneal perforation; moderate to severe decreased vision, loss of they eye.
TESTS AND DIAGNOSIS
Slit lamp examination is essential. Corneal scrapings for smears and cultures may be indicated. A corneal biopsy may be helpful if cultures are negative and the condition is worsening. Anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) imaging may be helpful to determine the extent of the infection.
TREATMENT
Corneal infections are treated with appropriate antibiotic, anti-fungal or anti-acanthamoeba medications. Dilating drops are often used. Glaucoma medications may be needed. In severe cases not responding to medical treatment, amniotic membrane tissue may be placed on the eye, or a corneal transplant may be required.
PREVENTION
Eye protection when engaged in risky activities. Remove contact lenses whenever the eye is red or irritated. Seek urgent ophthalmic care if ocular symptoms persist.