There are many causes of red eye which can range from mildly annoying to vision-threatening. The most common causes of red eye are infections, inflammation, allergies, and trauma. The eye may be red from a process affecting the outer structures of the eye, which includes the cornea, conjunctiva or eyelid, or an intraocular process (from inside the eye). The eye can often look the same from the outside despite different causes of red eye. Proper diagnosis and management require a full eye examination. This is a brief review of some common causes of red eye in children.

VIRAL INFECTIONS
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella-zoster virus (VZV) are rarer causes of red eye. These viruses can infect the front of the eye, known as the cornea. This generally causes significant eye pain and sometimes a change in vision. These infections typically effect only one eye and may result in permanent scarring in the eye and require examination to guide treatment.
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
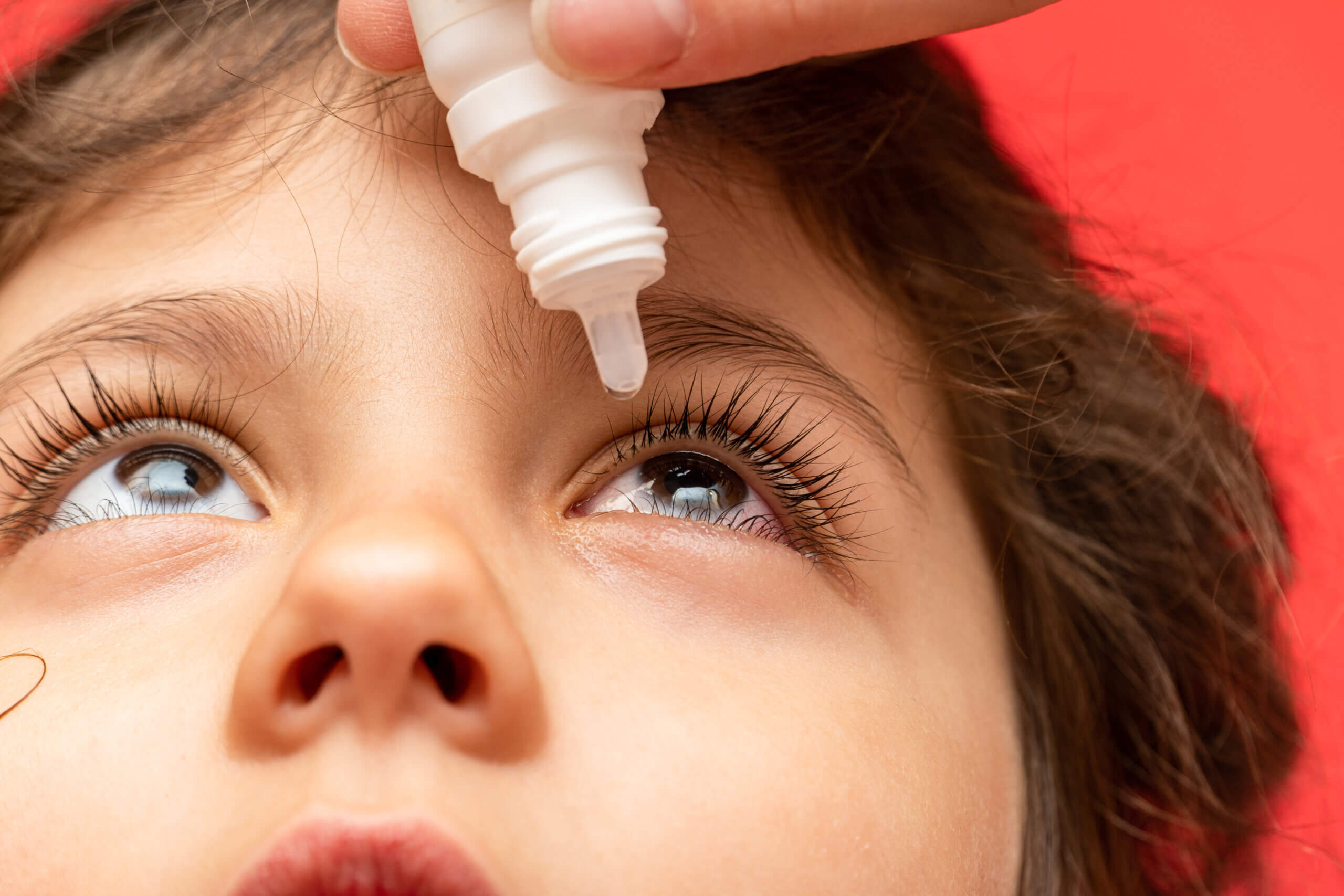
Allergic conjunctivitis is characterized by redness, intense itching and at times swelling of the eyelids.
Allergic reactions to environmental allergens like pollen, contact dermatitis, or insect bites, can cause a red eye. Removing the inciting factor and treating with antihistamine drops and cool compresses helps relieve symptoms.
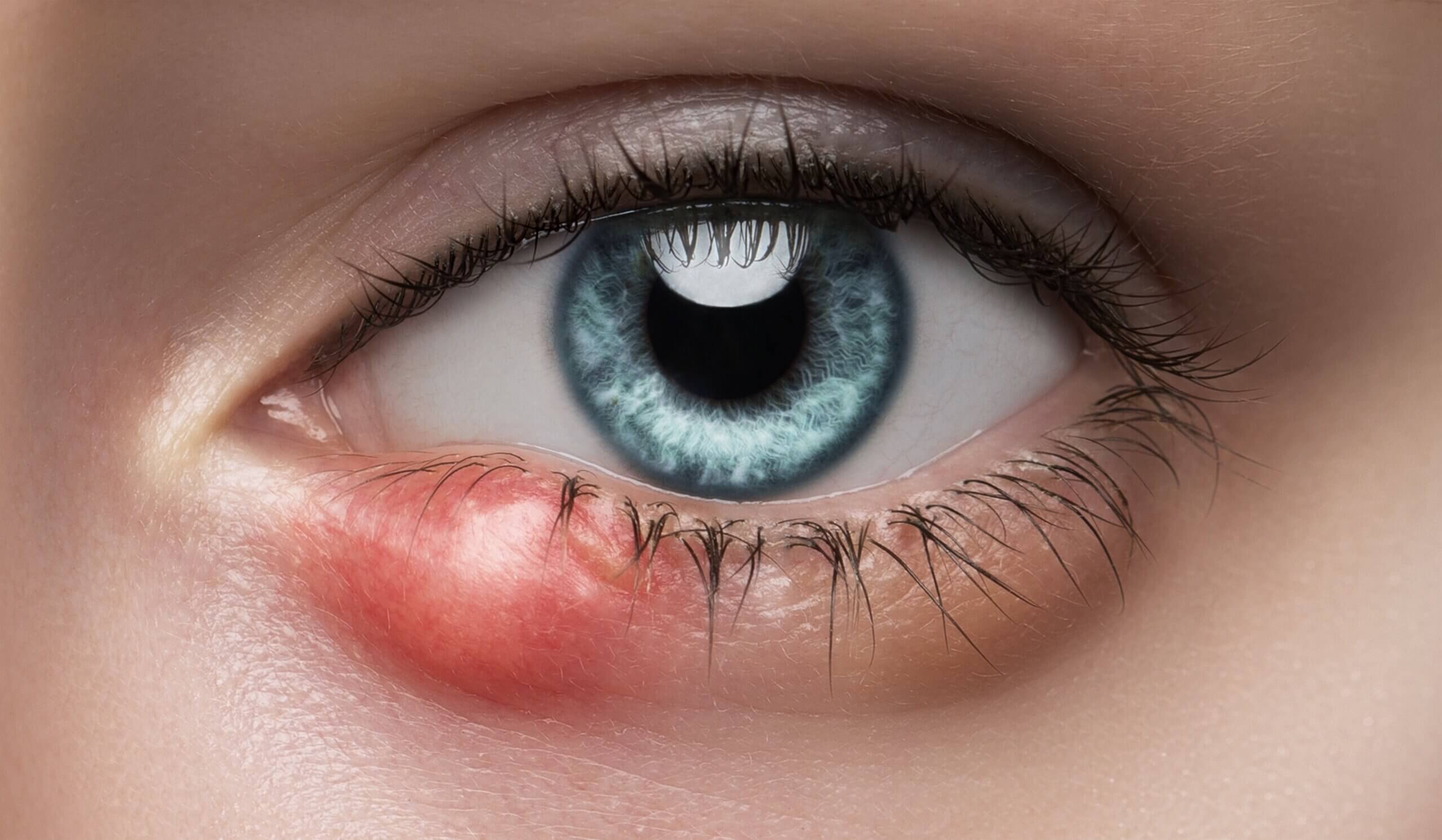
Blepharitis, or inflammation of the eyelid margin, can also cause red eyes, tearing, mild swelling or a reddish hue to eyelids, and a gritty sensation in the eyes. Styes or lumps on the eyelid may be common.
Iritis or uveitis occurs with inflammation from inside the eye. Although it is more common in one eye, but both eyes may be involved in children. This may cause eye pain, sensitivity to light, floaters, and blurred vision. There may be other parts of the body that are also affected. This requires an emergent eye evaluation.
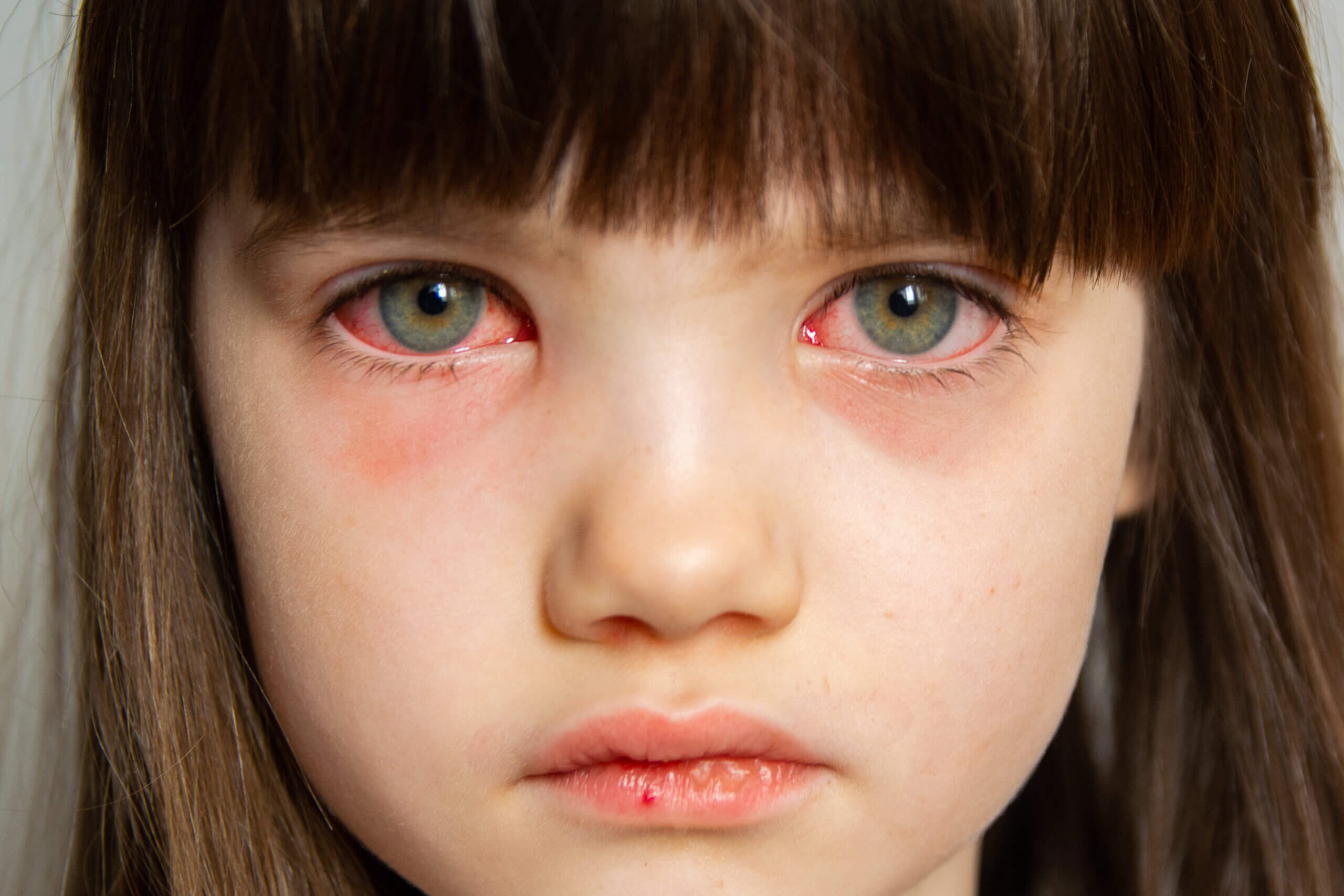
Trauma may be limited to the outer surface of the eye such as corneal abrasions (scratches), or corneal ulcers (infection). Careful examination is required to rule out retained foreign particles on the surface. Abrasions and infections may result in severe pain, tearing, foreign body sensation, and a change in vision.
Blunt trauma may cause bleeding inside the eye, resulting in hyphema. A hyphema is a visible pool of blood that collects inside the eye. It requires an emergent evaluation.
Chemical exposure can cause eye pain and redness. If your child’s eyes have been exposed to chemicals, it is important to irrigate them quickly and thoroughly with water. Tap water is fine. A full eye examination is necessary.












